Cardiovascular risk factors and low physical fitness associated with decline in social cognitive functions

A study collaboration has exposed that cardiovascular hazard variables (being overweight and large blood pressure) and lower physical fitness are related with lessened social mind network-connected neural action, which triggers social cognitive features to decline.
This suggests that getting a healthy life-style is not only valuable for condition prevention but also for protecting and increasing sociability. It is hoped that future exploration will direct to the growth of proposals for economical intervention methods through investigations into the success of interventions that goal cardiovascular risk elements and fitness (e.g., workout/well balanced food plan applications) on social cognition.
This collaborative examine was performed by research team that provided Assistant Professor Ishihara Toru (Graduate College of Human Advancement and Environment, Kobe University) and Professor Matsuda Tetsuya (Tamagawa College Mind Science Institute).
These benefits were revealed in the American College of Sports activities Medicine’s journal Medicine and Science in Sports activities & Exercise on June 6, 2022.
Weight problems has tripled in the previous 40 a long time, and because of to this and other contributing elements, the consequent raise in the selection of folks at danger for cardiovascular ailment has been declared a lead to for public health concern (WHO, 2021). In addition, there is also facts indicating that people’s cardiorespiratory stamina has been lowering above the past 40 yrs (Lamoureux et al., 2019, Sports Med). Prior analysis has demonstrated that lessened cognition (memory, recognition and so forth.) is connected with cardiovascular hazard variables and lower fitness degrees (Yang et al, 2018, Neurosci Biobehav Rev Colcombe & Kramer, 2003, Psychol Sci).
Even so, this kind of analysis had but to emphasis on social cognition, which kinds the foundation for social interactions. Social cognition is considered to engage in an vital function in our social life and psychological health. In the recent conditions, in which the quantity of people at threat of cardiovascular disorder and all those with minimal fitness ranges are expanding, locating out no matter whether or not these persons are also at risk of lowered social cognition is a urgent problem. With this in head, the study team made use of functional magnetic resonance imaging knowledge to investigate the relationship in between cardiovascular hazard variables, fitness and social cognition.
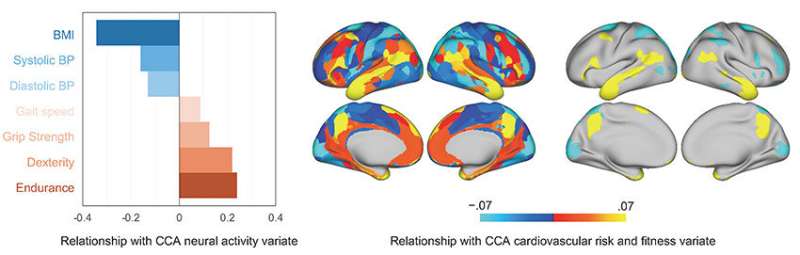
This study analyzed the knowledge of 1,027 individuals registered in the Human Connectome Project’s databases (U.S.). For the cardiovascular risk elements, the scientists applied Physique Mass Index (BMI), which is calculated from each person’s top and body weight, and systolic and diastolic blood force information. As indicators of fitness, the scientists utilized respiratory stamina, gait speed, hand dexterity, and grip energy (calculated utilizing the NIH Toolbox). To assess social cognitive purpose, they applied animacy perception precision, and the reaction moments and percentage of right answers for the emotion recognition job. Brain exercise through social cognition (i.e., throughout animacy notion) was calculated employing functional magnetic resonance imaging.
The analysis group then applied the gathered facts to look into the partnership amongst brain exercise all through social cognition and cardiovascular threat aspects/physical fitness. Later on, they investigated how brain exercise through social cognition mediates the relationship between cardiovascular risk components/fitness and social cognitive features.
The better the BMI/blood stress and the lessen the fitness concentrations of the subject, the lower their neural exercise amounts were being in the social mind network (temporo-parietal junction, temporal lobe, inferior frontal gyrus and posterior cingulate cortex) through social cognition (Determine 1). Between these associations, BMI, stamina and hand dexterity in certain had been located to be strongly connected to this lower in neural exercise.
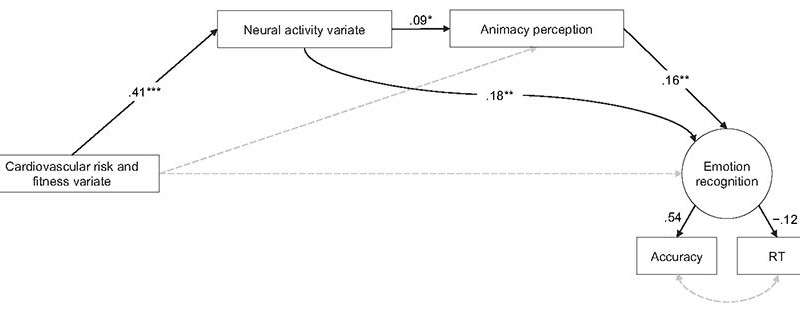
In addition, they identified that cardiovascular risk variables/fitness degrees, by using neural activity during social cognition, were being related to the precision of animacy notion and emotion recognition activity effects (Figure 2). These outcomes show that high BMI/blood tension and low fitness levels are connected with social cognitive drop by way of diminished social mind network-associated neural action.
This study did not illuminate the result in and outcome (i.e. Do cardiovascular danger factors and minimal physical fitness result in a drop in social cognitive features? Or do small social cognitive features guide to cardiovascular danger factors and low physical fitness?). In buy to investigation irrespective of whether or not a healthy life-style (workout and a balanced diet plan and many others.) can strengthen social cognitive features, it would be needed to inspect the benefits of real interventions. In individual, BMI, endurance and hand dexterity were uncovered to be strongly linked to social cognitive capabilities, hence it can be assumed that very efficient interventions to focus on weight loss and enhance endurance and dexterity would guide to improvements in social cognitive functions.
A 30-calendar year study backlinks childhood being overweight and fitness to midlife cognition
Toru Ishihara et al, Association of Cardiovascular Chance Markers and Fitness with Activity-related Neural Activity during Animacy Notion, Medicine & Science in Sporting activities & Training (2022). DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002963
Quotation:
Cardiovascular threat components and low physical fitness involved with decrease in social cognitive functions (2022, June 30)
retrieved 4 July 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-06-cardiovascular-aspects-bodily-decline-social.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any honest working for the objective of private research or investigate, no
section might be reproduced devoid of the prepared permission. The articles is provided for facts applications only.








